Parathyroid Hormone (PTH) Test
A parathyroid hormone (PTH) blood test measures the level of parathyroid hormone in the blood. This test is used to help identify hyperparathyroidism and hypoparathyroidism, to find the cause of abnormal calcium levels, or to check the status of chronic kidney disease. PTH controls calcium and phosphorus levels in the blood.
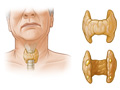
PTH is made by the parathyroid glands, which are four pea-sized glands that lie behind the thyroid gland. If the blood calcium level is too low, the parathyroid glands release more PTH. This causes the bones to release more calcium into the blood and reduces the amount of calcium released by the kidneys into the urine. Also, vitamin D is converted to a more active form, causing the intestines to absorb more calcium and phosphorus. If the calcium level is too high, the parathyroid glands release less PTH, and the whole process is reversed.
PTH levels that are too high or too low can cause problems with the kidneys and bones and cause changes in calcium and vitamin D levels.
Tests for calcium and phosphorus levels in the blood may be done at the same time as a PTH test.
Why It Is Done
A test for PTH is done to:
- Help identify hyperparathyroidism (an overactive gland) and hypoparathyroidism (an underactive gland).
- Find the cause of an abnormal blood calcium level.
- Check to see whether a problem with the parathyroid glands is causing the abnormal calcium level.
- Watch for problems in people who have chronic kidney disease.
How To Prepare
In general, there's nothing you have to do before this test, unless your doctor tells you to.
How It Feels
When a blood sample is taken, you may feel nothing at all from the needle. Or you might feel a quick sting or pinch.
Risks
There is very little chance of having a problem from this test. When a blood sample is taken, a small bruise may form at the site.
Results
Results are usually available in 1 to 2 days.
Normal
Each lab has a different range for what's normal. Your lab report should show the range that your lab uses for each test. The normal range is just a guide. Your doctor will also look at your results based on your age, health, and other factors. A value that isn't in the normal range may still be normal for you.
High values
High PTH levels may be caused by:
- A parathyroid gland growth (hyperplasia) or a parathyroid tumor.
- A low level of calcium in the blood. A low blood calcium level can be caused by kidney disease, kidney failure, severe vitamin D deficiency, or an inability of the intestines to absorb calcium from food.
- Some types of cancer, such as lung, kidney, pancreatic, or ovarian cancer.
Low values
Low PTH levels may be caused by:
- Damage to the parathyroid gland, which can by caused by neck surgery or radiation treatments.
- A rare disease, such as sarcoidosis or histiocytosis X.
- An overdose of vitamin D or calcium.
- Cancer, such as lymphoma or multiple myeloma.
- A low magnesium level.
Credits
Current as of: September 25, 2025
Author: Ignite Healthwise, LLC Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Ignite Healthwise, LLC education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.